One way to gauge the health of Galveston Bay is to assess the levels of life-sustaining nutrients and oxygen. Too many nutrients can cause algae blooms that deplete oxygen and harm aquatic life. However, plant life which is an important link of the bay’s food web requires nutrients. Water quality grades in the 2024 Report Card reflect conditions in the Bay and its watersheds in 2023. The levels of nutrients and dissolved oxygen found in the 2023 samples were overall at acceptable levels for supporting diverse and healthy aquatic life. The water quality issues that do arise are primarily due to runoff and wastewater from human activity.
Water Quality Summary
What We Can do
- Follow these tips for organic lawn care on the upper Texas coast. Going organic can save you money and keeps toxic chemicals out of the environment and out of our waterways.
- Slow your runoff by reducing paved areas and installing rain barrels.
- Pick up after your pets and properly dispose of pet waste.
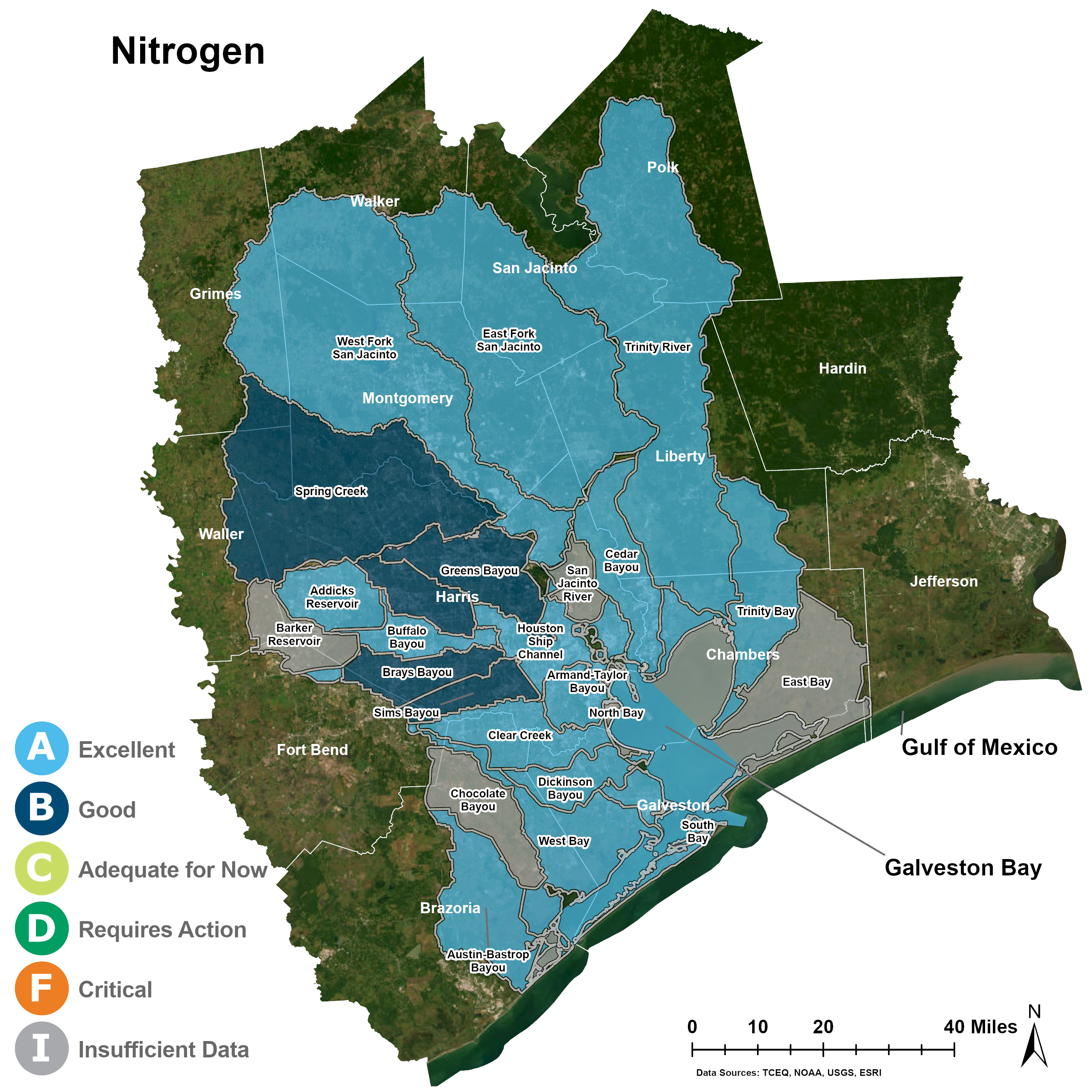
Nitrogen
Many watersheds in the Galveston Bay region receive an A grade, and most watersheds did have enough samples for a grade, unlike in 2020 and 2021.
Nitrogen in Water
What We Can do
Keep Excess Nitrogen Out of Our Waterways
- Follow fertilizer directions carefully and don’t overfertilize. Going organic is a great way to reduce the amount of fertilizer you use!
- Leave as much of your property unpaved as possible.
- Plant a rain garden that collects rainwater and allows it to soak into the soil.
Galveston Bay Nitrogen
Rivers and Bayous Nitrogen
Be frugal with water and fertilizer use – Don’t fertilize your local waterway
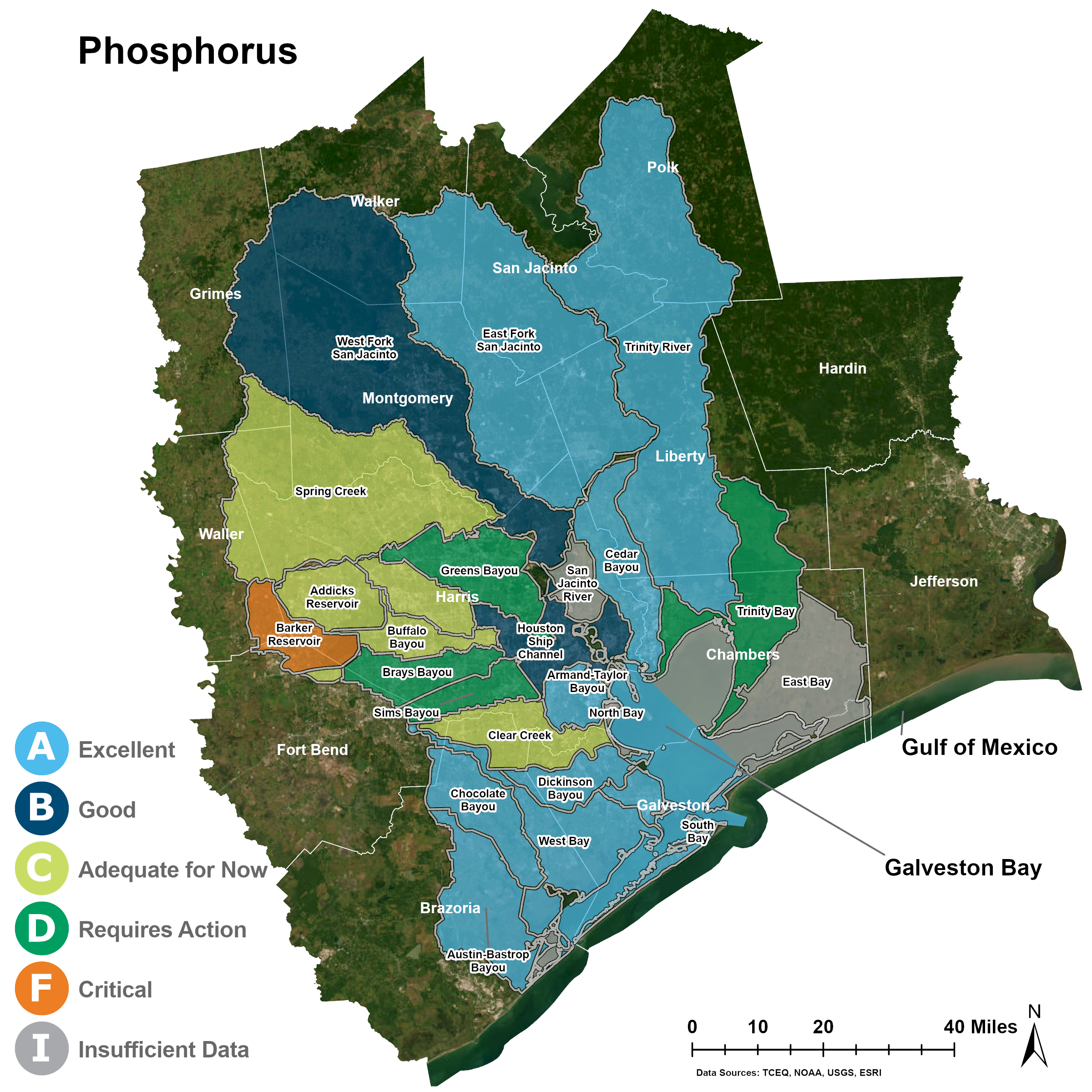
Phosphorus
In 2023, the watersheds in the Galveston Bay region received A’s, B’s, C’s, D’s and one F. Brays Bayou, Greens Bayou, Sims Bayou, and Trinity Bay watershed all received D’s; while Barker Reservoir received an F grade.
Phosphorus in Water
What We Can do
Keep Excess Phosphorus Out of Our Waterways
- Use phosphate-free or phosphate-reduced laundry, dish, and car-washing soaps.
- Incorporate landscaping techniques that require less fertilizer, like growing a garden with native plants.
- Control erosion. Phosphorus attaches to soil particles, making erosion a contributor to phosphorus pollution.
Galveston Bay Phosphorus
Rivers and Bayous Phosphorus
Water sparingly and apply the correct amount of fertilizer to reduce lawn care cost
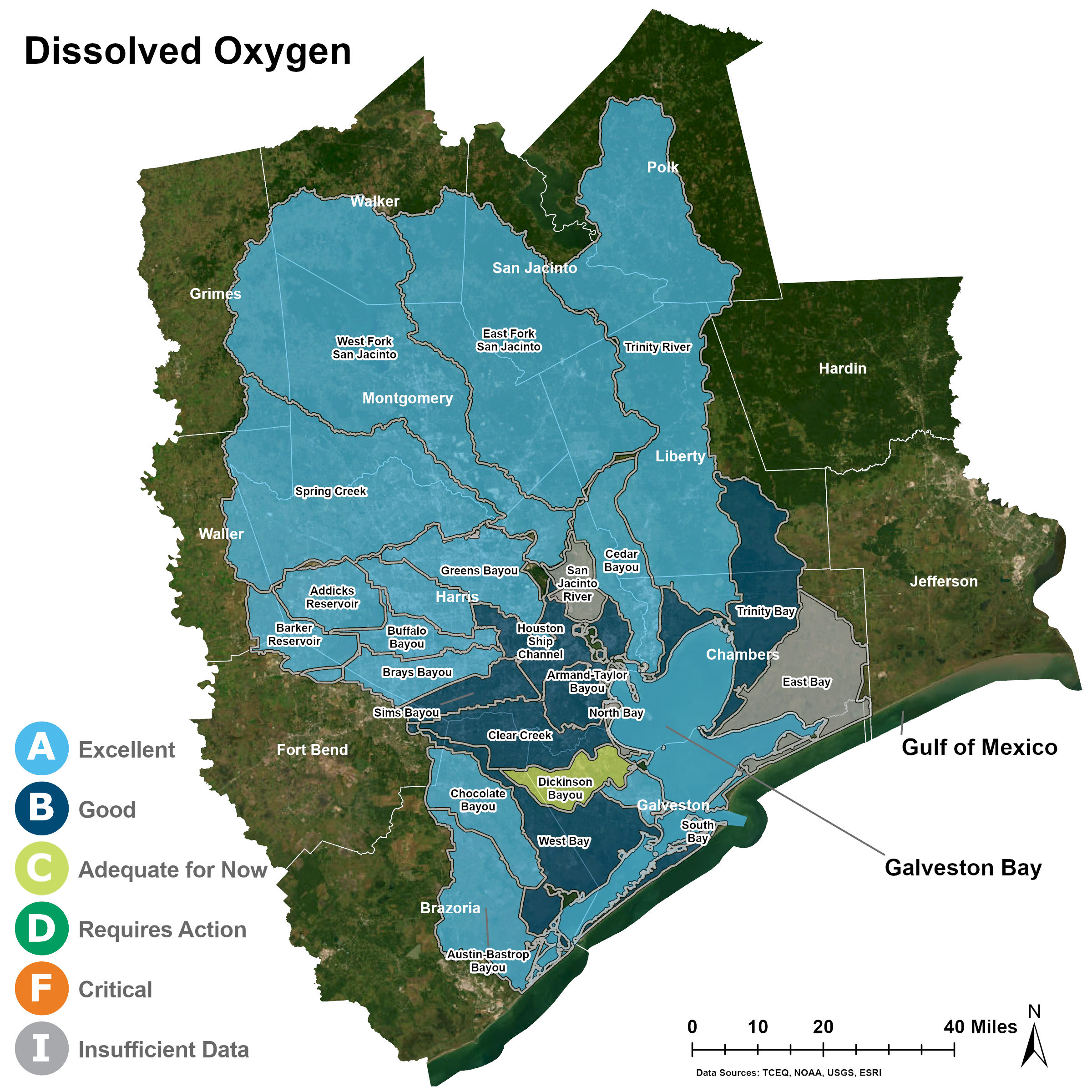
Dissolved Oxygen
Just as people need oxygen to breathe, adequate oxygen levels in water are required to support aquatic life in Galveston Bay and area bayous. Hypoxia (low-oxygen) and anoxia (no-oxygen) zones are common after large algae blooms in water that is warm, still, and has poor clarity. Benthic (bottom-dwelling) organisms can’t escape or survive in hypoxic conditions. In 2023, dissolved oxygen one percent of samples collected in Galveston Bay had dissolved oxygen levels below the screening levels set for the protection of aquatic life. Levels were below state screening levels in only 18 percent of samples collected from the rivers and bayous surrounding the Bay. As a result, all of Galveston Bay continues to receive an A grade for dissolved oxygen. This is good news for the Bay and its fish and shellfish populations.
Dissolved Oxygen in Water
What We Can do
Our Actions Impact Oxygen Levels
- Help preserve and restore habitats that help promote high oxygen levels, like forests and wetlands.
- Help prevent nutrient pollution by following the steps above to reduce nitrogen and phosphorus levels in Galveston Bay.
- Find out what else you can do about nutrient pollution.
Galveston Bay Dissolved Oxygen
Tributary Dissolved Oxygen